第5章 数组
- 元素个数是常量,不能是变量
- 复制数组:需要逐一复制每个元素
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//逆序排列整数数组
int array_int[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int array_size = sizeof(array_int) / sizeof(array_int[0]);
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < array_size; i++) { cout << array_int[i] << ' '; }
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < array_size / 2; i++) {
temp = array_int[i];
array_int[i] = array_int[array_size - i - 1];
array_int[array_size - i - 1] = temp;
}
for (int i = 0; i < array_size; i++) { cout << array_int[i] << ' '; }
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
*/
多维数组:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int multi_array[2][3][4];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++){
multi_array[i][j][k]=i+j+k;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
cout<<multi_array[i][j][k]<<' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
/*
0 1 2 3
1 2 3 4
2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4
2 3 4 5
3 4 5 6
*/
第6章 函数
- abort(): 强制结束
- exit(0); 正常结束程序
针对整数内部的二进制的4种位运算:
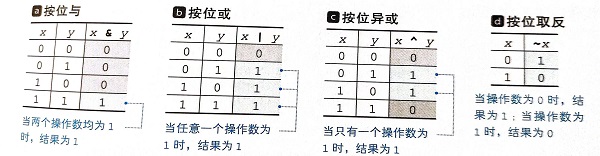
位移运算符:
- x<<y:返回 x的所有二进制位向左移动y位后的值
- x>>y:返回 x的所有二进制位向右移动y位后的值
正常的函数参数是值传递,并不会修改原始参数.
在变量类型后添加& 定义的变量为引用变量,该变量引用的变量享有同样的地址是引用变量的别名。应该谨慎使用引用传递,因为会修改调用函数的值。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap1(int a, int b) {
// 只会在该函数内部修改值,不会修改调用函数传入的值
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
void swap2(int& a, int& b) {
// 在该函数内部修改的值会修改调用函数传入的值,因为该函数内的变量是调用函数的变量的别名
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
int main() {
int x = 2, y = 3;
cout << "x=" << x << ",y=" << y << endl;
swap1(x, y);
cout << "x=" << x << ",y=" << y << endl;
swap2(x, y);
cout << "x=" << x << ",y=" << y << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
x=2,y=3
x=2,y=3
x=3,y=2
*/
作用域:
- ::x , 访问全局的作用域
- x::y,访问命名空间x中的y
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int x = 100;//global var
int main() {
int x = 50;
cout << "x=" << x << endl;
for (int x = 0; x <= 10; x++) {
if (x % 6 == 0)cout << "x="<<x << endl;
}
cout << "x=" << x << endl;
cout << "x=" << ::x << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
x=50
x=0
x=6
x=50
x=100
*/
静态存储期
变量的生命周期称为存储期,有三种:
- 静态存储期:在函数外声明并定义的对象,或在函数内声明为static 的对象,会在执行main函数的准备阶段创建,在程序结束时销毁。 声明static 变量时是可以使用变量的
- 自动存储期:在函数中定义的不带static的对象,会在程序流执行声明语句时创建,在通过包含声明块的}时销毁。 用register 声明的变量也会赋予自动存储期,register 是C语言的遗留物,C++中几乎不用。
- 动态存储期
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int fx; //静态存储期,初始化为0
int main() {
static int sx;//静态存储期,初始化为0
int ax;// 自动存储期,初始化的值不确定, 未初始化会报错: 使用了未初始化的局部变量“ax” mjcpp
ax = 10;
cout << "fx=" << fx << endl;
cout << "sx=" << sx << endl;
cout << "ax=" << ax << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
fx=0
sx=0
ax=10
*/
静态存储期变量只会初始化一次:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int fx; //静态存储期,初始化为0
void func() {
static int sx = 0; // 函数第一次被调用时初始化sx的值
int ax = 0;
fx++;
sx++;
ax++;
cout <<setw(4)<< fx << setw(4) << sx << setw(4) << ax << endl;
}
int main() {
cout << " fx sx ax\n------------\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)func();
return 0;
}
/*
fx sx ax
------------
1 1 1
2 2 1
3 3 1
4 4 1
5 5 1
6 6 1
7 7 1
8 8 1
9 9 1
10 10 1
*/
函数的返回值为static时,用type& func() 定义函数时,函数名fanc()返回对应的值。
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int fx; //静态存储期,初始化为0
int& func1() {
static int x;
x *= 2;
return x;
}
int& func2(int idx) {
// idx 为坐标
static int a[5];
return a[idx];
}
int main() {
func1() = 1; //初始化为 x=1
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
func1();
cout << "func1()=" << func1()<<endl;
}
/*
func1()=4
func1()=16
func1()=64
func1()=256
func1()=1024
*/
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
func2(i) = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << "func2(" << i << ")=" << func2(i) << endl;
}
/*
func2(0)=0
func2(1)=1
func2(2)=2
func2(3)=3
func2(4)=4
*/
return 0;
}
函数重载
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int max(int a, int b) {
if (a > b) return a;
return b;
}
double max(double a, double b) {
if (a > b) return a;
return b;
}
int max(int a, int b,int c) {
int max = a;
if (b > max) max = b;
if (c > max) max = c;
return max;
}
double max(double a, double b, double c) {
double max = a;
if (b > max) max = b;
if (c > max) max = c;
return max;
}
int main() {
int a = 3, b = 8, c = 10;
float d = 4.0, e = 5.5, f = 10.141;
double i = 4.0, j= 5.5, k = 10.141;
cout << "max(a,b)=" << max(a, b) << endl;
cout << "max(a,b,c)=" << max(a, b,c) << endl;
cout << "max(d,e,f)=" << max((double)d, (double)e,(double) f) << endl; // 需要转为参数需要的类型
cout << "max(i,j,k)=" << max(i, j, k) << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
max(a,b)=8
max(a,b,c)=10
max(d,e,f)=10.141
max(i,j,k)=10.141
*/
正文完